Classroom Activities
Problem Set I: Problems that only involve whole numbers in the given data and are represented by:
ax + b = d (Eq. 1b)
- Remy went to the convenience store to get ice cream. She selected four small containers and paid a $20 bill for them. She got $10 in change. What was the price of a container of ice cream that Remy bought?
- Rosa stopped at a fruit stand to buy some pears. She got Asian pears at $3 per pound. She paid with a $10 bill and got $1 in change. How many pounds of pears did she buy?
- At the office store, Roger bought some notebooks for $3 each and a package of pencils, which cost $2. The total cost of the buy was $20. How many notebooks did Roger buy?
- Jeff was window shopping. In one window, he saw a display of neckties arranged in rows of 5 neckties each. Additionally, there were two exceptional neckties on the right-hand side. Suppose there were 32 ties in the window. How many rows of neckties were there?
- Jeff was window shopping. He saw a display of neckties arranged in 8 rows in one window. Additionally, there were 4 unique neckties on the left-hand side. Suppose there were 60 ties in the window. How many neckties were in each row?
- A school arranged a picnic on the field day. Every student got a plastic fork, a plastic spoon, and a plastic cup. After giving all students their utensils, there were 30 plastic items left saved for another event. The students were very neat and put all the used utensils in a large trash can. At the end of the picnic, the trash had 300 single-use plastic items. How many students were at the picnic?
- Jose put some stickers in a sticker book of superheroes. He put five stickers on each page, except for the last one, which took seven, and he used 62 stickers in all. How many pages were in the sticker book?
- Jose put some stickers in a sticker book of superheroes. It had 13 pages in all. Every page took the same number of stickers, except for the first page, which took two 2 more stickers than the other pages. In all, Jose used 80 stickers. How many stickers were on the typical page?
- Paula bought five dozen flower bulbs to plant in the garden patch in front of her house. She planted four bulbs along the walkway to the front door. The rest, she arranged in rows parallel to the front of the house. She put eight bulbs in each row. How many rows was she able to make?
- Clark bought five dozen flower bulbs to plant in the garden patch before her house. She planted four bulbs along the walkway to the front door. The rest, she arranged in seven rows parallel to the front of the house. How many bulbs were in each row?
Problem Set II: Problems that only rational numbers in the given data and are represented by
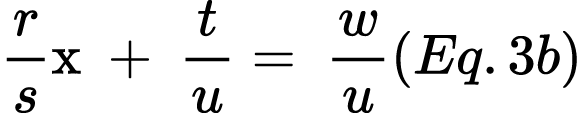
- Sara prepares a cake for his mother’s birthday. The recipe requires 2/3 cup of flour for every person. Her little brother is helping her, measuring the flour using a 1/4 cup. He discovers they have 25 measuring cups of flour (or 25/4 cups). After preparing the cake, they have ¼ of a cup of flour left. The cake was made for how many people?
- Paul buys some pounds of apples at ½ $ per pound. He pays with 5 dollars and receives 2 dollars in change. How many pounds of apples did he buy?
- Karla buys ¾ pounds of grapes. She pays with 2 dollars and receives 50 cents (1/2 dollar) in change. What is the cost per pound of the grapes?
- Jill bought 4/5 lb. of grapes at x $ per lb. She paid with a 10-dollar bill and received 2 dollars in change. What is the price of the grapes per pound?
- Every morning, Mary walks at a pace of 20/7 miles per hour. On Monday, she was planning to walk 4 miles. However, she had to stop when she still had one mile left after she realized she had an early meeting at work. How many hours did she walk on Monday?
- Peter swims at a pace of 4/3 mph. His trainer programs three hrs. sessions; however, Paul had to stop swimming 30 minutes before completing the session because the summer camp needed a lifeguard. How many miles did Peter swim?
- Every morning, Elisa serves fruits for breakfast in her school cafeteria. On Tuesday, she noted that students only eat ¾ of each fruit. After collecting all the remainder, she made 12 whole apples. How many fruits did she serve?
- Carlos sets tables, each with four chairs, for a school dance. He noticed that only 2/3 of the tables were occupied during the party, although these were full. If 20 students did not attend the party out of the 60 invited, how many tables did Carlos prepare?
- John prepares a jelly for his class. The recipe requires 2/3 cups of the mix for every person, and he has 23 cups of it. After preparing the jelly, he had only 1/3 cup of the mix left. The jelly was made for how many people?
- Laura bought 8/3 lbs. of avocado at x $ per lb. She paid with a 5-dollar bill and received 1-dollar in change. What is the price of avocados per pound?
Problem Set III: Problems that only rational numbers in the given data and are represented by
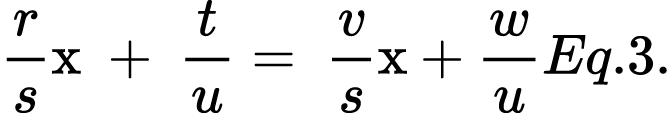
- Maria and John are planting flowers in their respective gardens. Each has chosen a different type of flower, and they plant at different rates.
- Alice and Bob drive west on the Mass Turnpike (I90). They are both on their way to a concert at Tanglewood. Alice is driving one (=4/4) mile a minute and has 40 miles to go. Bob drives at 5/4 miles per minute and has 50 miles to go. How long will it take Bob to catch up to Alice? And how far from Tanglewood will they be?
- Alice and Bob are filling a swimming pool with water from two sources. They each have a different flow rate and want to determine when the water levels from both sources will be the same so they can go together for lunch. Alice's source fills the pool at a rate of 2/5 of the pool's capacity per hour, and she has already filled 1/10 of the pool. Bob's source fills the pool at a rate of 1/5 of the pool's capacity per hour and has already filled 3/10 of the pool.
- Samantha is selling handcrafted necklaces. Each necklace is priced at 3/4 of a dollar. She has already earned 4/2 dollars today from other sales. Lucas, on the other hand, is selling bracelets. Each bracelet is priced at 2/4 of a dollar. He has already earned 8/2 dollars today from other sales. They are curious to know after how many items sold they will both have the same earnings for the day.
- Emily is conducting a chemistry experiment in her lab. She wants to have two beakers with the same amount of a certain chemical in both. The chemical is a solute – it is dissolved in water. One beaker already has 5/9 grams of the chemical, and another has 1/9 of a gram. She also has some bottles with the chemical dissolved in different concentrations. Bottle A has 3/7 of a gram of solute per milliliter of solution, and bottle B has 5/7 of a gram of solute per milliliter of solution. She wants to add the same volume of solution from each bottle to each beaker (the bottle with higher concentration to the beaker with less solute), to equalize the amount of solute in the two beakers. How many milliliters should she add?
- Samantha and Emily are both running on a circular track. Samantha starts at a point of 2/5 on the track and runs at a rate of 5/12 of the track per minute. Emily starts at a point 1/5 on the track and runs faster, at a rate of 7/12 of the track per minute. How long (how many minutes) will it take for Emily to catch up to Samantha?
- Jamie went to a candy store where all the candies were sold at a fixed price per pound. Jamie bought some hard candies weighing 4/5 pounds and some gummy bears weighing 1/5 = 3/15 pounds. At the same time, Alex bought hard candies that weighed a total of 3/5 pounds and then added a larger type of gummy bear to his purchase. A big gummy bear weighs 4/15 pounds. If Jamie and Alex bought the same total candy weight, how many gummy bears did each one buy?
Maria and John have small gardens in the yard of their apartment building. They both grow flowers, although different kinds. Today, they are planting their gardens. John works more slowly than Maria, but he starts sooner. At the moment, John has planted 2/3 of his garden, but Maria has only planted 1/3. John can plant 1/8 of his garden each hour, and Maria can plant 3/8 of hers each hour. They agree that they will take a break and go for coffee when they have the same portion of their gardens left to plant. How long from now will that be? And how much will each have left to plant?
Solutions to selected problems from Problem Set III.
(1) Let x be the number of hours at which they will have planted the same portion of their gardens; then,
1/8 x + 2/3 = 3/8 x + 1/3
x = (2/3) – (1-3) / (3/8 – 1/8)
x = (1/3) / (2/8)
x = (1/3) * (8/2) = 8/6 = 4 /3 hrs.
(2) Let x be the number of minutes it takes for Bob to catch up to Alice; then,
(4/4) x + 10 = (5/4) x
10 = ((5 /4) – (4/4)) x
10 = (1/4) x
x = (10 / 1) / (1 /4) = (10 /1) *(4 /1) = 40 minutes
The total distance is (4/4) *40 + 10 = 50 miles. Thus, they will be right at Tanglewood!
(4) Let x be the number of items, then,
¾ x + 4/2 = 2/4 x + 8/2
x = (8/2) – (4/2) / (3/4) – (2/4)
x = (4 / 2) / (1 /4) = (4 / 2) * (4 /1) = 16/2 = 8 items.
(5) Let x be the number of milliliters, then,
5/9 + 3/7 x = 1/9 + 5/7 x
x = (5/9) – (1/9) / (5/7) – (3/7)
x = (4/9) / (2/7) = (4/9) *(7/2) = 28/18 = 14 /7 ml

Comments: