Background Information
This section contains content knowledge about the different types of energy sources.
Fossil Fuels
“Currently, over 80% of the energy used by mankind comes from fossil fuels.” (Department of Energy 2024) While many enjoy the benefits of fossil fuels, not everyone uses them. Unfortunately, the waste products from the combustion of fossil fuels affects everyone on the planet. For example, burning fossil fuels contribute 30 Gt of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere each year and this has triggered climate change. Additionally, the transportation and mining of fossil fuels in the ocean have had leaks that have killed ocean wildlife and affected the water quality. Fossil fuels are relatively cheap, and many rely on them to meet their energy needs. Fossil fuels are very popular for developed, and developing, countries because they are accessible all over the world, they are efficient, make fuel for transportation, are relatively cheap, and can be converted from solid to liquid or gas fairly easily. Fossil fuels also have an established infrastructure and industry.
In 1855, the Silliman Report disclosed the findings of Benjamin Silliman, Jr. from his experiments with petroleum. These experiments were performed as a result of the energy crisis of that time period of using whale oil in lamps to light homes at night. The whale population was being depleted and a solution was needed. Benjamin Silliman Jr. found that petroleum can be distilled into different substances. One of those substances was kerosene and the other was gasoline. The kerosene was a great substitute for the whale oil and at that time, the gasoline was discarded. Unfortunately, it was usually thrown away in a river which was disastrous for the environment. Thankfully, scientists found a use for gasoline. Gasoline has a lot of stored energy and is easily portable. Instead of throwing it in a river, gasoline is a great way to fuel the combustion engine of our vehicles. The conclusion of Silliman’s experiments resulted in the start of the petroleum age and our dependence on fossil fuels for our energy needs. (Reuben A. Holden, Secretary of Yale University, Records (RU 19). Manuscripts and Archives, Yale University Library.).
Fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas are the remains of prehistoric plants and animals that died and were buried under sediments millions of years ago. Depending on the type of plant or animal, the temperature, the pressure, and how long it was buried determined the type of fossil fuel created. These resources are mined from deep underground and burned to produce electricity or refined to be made into fuel for transportation or heating. (Department of Energy 2024) After these resources are mined, they are processed for our energy needs. For example, “In conventional power plants, pulverized coal is burned in a boiler, where heat vaporizes water in steam tubes. The resulting steam turns the blades of a turbine, and the mechanical energy of the turbine is converted to electricity by a generator. Waste gases produced in the boiler during combustion – among them, SO2, NOx and CO2 – flow from the boiler to a particulate removal device and then to the stack and the air.” (Fulkerson, William, Roddie R. Judkins, and Manoj K. Sanghvi. “Energy from Fossil Fuels.” Scientific American 263, no. 3 (1990): 128-35. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24996937.) The combustion of fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and is causing global warming because CO2 is one of the major contributing gasses in the greenhouse effect. Carbon dioxide traps heat from the sun that would have escaped back into space. We need some CO2 to stabilize our temperature, but too much CO2 in the atmosphere traps more heat than we need causing the global temperature to rise.
Solar
We can use the sun’s energy to produce electricity. Solar panels can be used to harvest energy from the sun. “Solar energy is an endless source of energy, which is ecologically clean and is not considered harmful.” (Jakhongir Turakul Ugli 2019) The sun’s energy has been used by humans as early as the 7th century B.C. to light fires by reflecting the sun’s rays onto shiny objects. The Greeks and Romans manipulated mirrors to focus the sun’s rays to light torches. In 1839, a French physicist named Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic (PV) effect while performing an experiment. He exposed a cell that was connected to metal electrodes and submersed in a conducting solution to a light source and noted that it produced more electricity. In 1954, PV technology was enhanced when Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson developed the silicon PV cell at Bell Labs. The first PV cell capable of converting the sun’s energy into electricity to power everyday equipment was created. Solar panels use a semiconductor, like silicon, encased in glass. The panel is exposed to the sun. The photons of sunlight cause an electron to be released and produce an electric charge. The charge creates an electric current, direct current (DC), which is captured by wires inside the panel. The DC is then converted to alternating current (AC) by an inverter. AC is the type of current we use to power our electric devices. (National Grid 2023b)
At any given time on the planet, we are using 18 terawatts of energy. If we could capture one hour of the sun’s energy striking the planet at any given time, then we could power the planet for one year. However, capturing and storing the sun’s energy isn’t an easy task. Solar panels can be expensive to produce and require several factors to operate at peak performance. Solar panels need land or space for installation, to be cleaned regularly, and angled towards the sun to receive direct sunlight. The sun moves across our sky and doesn’t shine at night and is less efficient on a cloudy day. Therefore, a system will need to be created to store the energy captured to be used when demand is high. In areas with a large installation of PV panels, such as Southern California, much of the energy produced by solar panels during the day can’t be used because there isn’t a high demand for the electricity (See Figure 1). Our electricity demand increases dramatically in the evening hours just before sun set and rises sharply through the evening and into the night. The demand decreases as we approach midnight and increases again when we wake up in the morning.
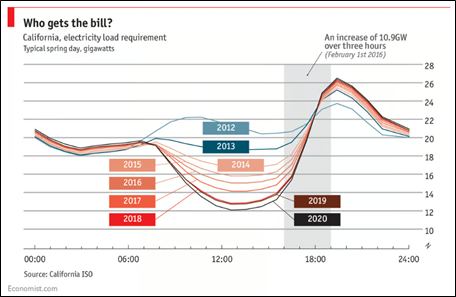
Figure 1 shows the energy demand in California on a typical spring day from 2012 – 2020. Source: https://www.economist.com/graphic-detail/2018/03/28/what-a-ten-year-old-duck-can-teach-us-about-electricity-demand
Using the sun’s energy is not only limited to solar panels. The sun can be used for thermal heat and cooking. A solar oven is a device that can be created in a variety of ways. Using household materials, you can create a small solar oven to cook simple items. Larger solar ovens can be created to cook larger items. There are many communities around the world that use the sun to cook their food. Some people use them when they are camping and do not have access to electricity.
Wind
“Man has harnessed the energy in wind for thousands of years, both for sailing boats and powering wind mills at land.” (Jaber 2014) As far back as 5,000 B.C., sail boats used the wind to navigate the Nile River in Egypt. Around 200 B.C., wind was used to pump water in China and grind grain in the Middle East. This technology has continued to grow, expand, and improve over time. Today, wind power is one of the leading solutions to our energy crisis.1
Wind energy generation is clean and renewable. It requires no fuel and has zero harmful emissions. Unfortunately, it can’t be used in many places due to its visual obstruction and threat to wildlife, and the wind doesn’t blow all the time. Wind turbines are usually white or pale grey to make them blend in with their environment. Some places require additional markings on the ends of the blades for visibility. There has been discussion about painting them green to help them blend in with the environment better.2
Wind energy can be captured on land or offshore. The potential for this resource is rapidly expanding. Offshore turbines are placed out in the ocean. On land, wind turbines are placed in fields or in rural areas where large buildings and obstructions don’t interrupt air flow. The very first wind turbine was created by Professor James Blyth in Scotland in 1887. It was ten meters high and had a sail cloth. The first wind farm opened in the United States in 1980 in New Hampshire. The wind industry has continued to grow and improve over time. Wind turbines vary in size and can be adapted for personal use or connected together to form a wind farm. Each wind turbine consists of two or three blades, a gear box called a nacelle and a shaft. When a gentle breeze or gust of wind makes the blades spin, electricity is generated. The kinetic energy generated from the rotation of the blades is transferred to the gear box and generator, which creates an electric charge. Most wind turbines operate between seven miles per hour (mph) and 56 mph and maximum efficiency is usually between 18 mph and 27 mph.3
Unfortunately, wind turbines have had a negative effect on the environments where they are placed. There have been habitat losses and disruption. Additionally, birds have collided with them and died. However, wind power’s impact on bird populations is relatively small when compared to the number of birds killed by cats and their collisions with high rise buildings. Additionally, in order for wind turbines to work, they need to be placed in a windy location. Not every location is a viable place for the implementation of a wind turbine to provide electricity. Wind energy is a type of solar energy. As the sun heats up the Earth, land and water heat at different rates. The differences in temperature create a convection current, causing the wind to blow. Also, the wind is intermittent and does blow all the time.3
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectric energy production is the most cost effective and is unlimited as long as the source remains available. It accounts for about 16% of energy production in the world today. (Bagher et al. 2015) Hydropower is a renewable energy source that uses a dam to alter the flow of a river to generate electricity. The hydropower source requires a constant replenishing from the water cycle. Electricity is generated by flowing water that has a change in elevation. The greater the elevation, the greater the kinetic energy of the flowing water and the greater the potential the create electricity. Flowing water turns turbines inside a generator that creates an electric current.3 Unfortunately, the building of dams has a negative effect on the surrounding environment and a dam failure can be catastrophic to the humans and animals that live near it. There have been numerous dam failures that have occurred throughout history. However, with proper maintenance, dam failures can be avoided.
Humans have been using water to perform work for thousands of years. The Greeks used it to grind wheat to make flour. In 1881, a water turbine in a flour mill provided street lighting at Niagara Falls, New York using direct current. In 1893, the Redland Power Plant used water wheels and a three-phase generator to create power. Over the years, a number of innovations have allowed hydropower to become an important part of the renewable energy options available to us. For example, alternating current allows the power generated by a water turbine to be transmitted across longer distances.4
The most famous source in the United States is the Hoover Dam built in 1936 on the border of Nevada and Arizona on the Colorado River. Hydropower accounts for about 6.2% of total electricity generation in the United States. All but two states (Delaware and Mississippi) use hydropower as a part of their electricity plan. The use of water generated power varies from state-to-state. For example, in 2020, the state of Washington used hydropower for about 66% of their electricity needs. Additionally, states like Washington, Idaho, and Oregon have lower energy costs than the rest of the country due to their use of hydroelectric power. The initial cost of installing a hydropower facility can be high, but that evens out over time. Hydropower has a long-life span and maintenance cost are relatively small. This results in hydropower being much more cost effective than other energy sources. Hydropower stations vary in size from Hoover Dam sized to tiny personal use. Not all hydropower comes from dams. Some use diversions or run-of-river facilities like an irrigation ditch.4
Geothermal
Geothermal energy is produced by heat conduction. Water transports the energy to the surface for utilization and then must be recharged. However, those sources can take a long time to recover. So, geothermal energy may not be renewable in most places. Geothermal energy can also be extracted from hot dry rock, but this is still in the experimental stages. (Stefansson, V. (2000, May). The renewability of Geothermal Energy. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress 2000 (pp. 883-888).
Geothermal heat pumps take advantage of the relatively constant temperature below the Earth’s surface at about 30 feet below ground where the temperature is typically between 50 oF (10 oC) and 59 oF (15 oC). So, the soil temperatures are usually higher than the air temperatures in the winter and cooler than the air in the summertime. Geothermal heat pumps exchange temperatures, efficiently heating homes in the winter and cooling them in the summer (See Figure 2). This method of heating and cooling is energy-efficient, environmentally clean, and cost-effective. It can be used in all types of buildings, not just homes.4


Figure 2: A geothermal heat pump extracts heat from the home in the summer and pumps heat into the home in the winter.6
There are hot water reservoirs all over the world. This water can be found at the surface, like a hot spring, or deeper down. The temperatures of these waters can range from 300 oF to 700 oF. The steam produced from these hot waters can be used to spin a turbine and create electricity.5
Currently, California has 43 geothermal plants with plans to build more. In Boise, Idaho, 92 of the biggest buildings in the city use geothermal heating. “A 2019 U.S. Department of Energy report, GeoVision: Harnessing the Heat Beneath Our Feet, says ‘generating electricity through geothermal methods could increase 26-fold by 2050, providing 8.5% of the United States’ electricity, as well as direct heat.”7
Biomass
Biomass is a renewable energy source. It has stored energy from the sun that is produced by plants through photosynthesis. It can be burned directly for heat, like burning a log in a firepit. It can also be converted to a liquid or gas. There are many different places to find a biomass source. For example: paper, corn, vegetable oil, animal fats, soybeans, sugar cane, algae, cotton, food scraps, human and animal waste (See Figure 3). Almost anything that benefits from photosynthesis has stored energy that can be converted to biomass through various processes.6
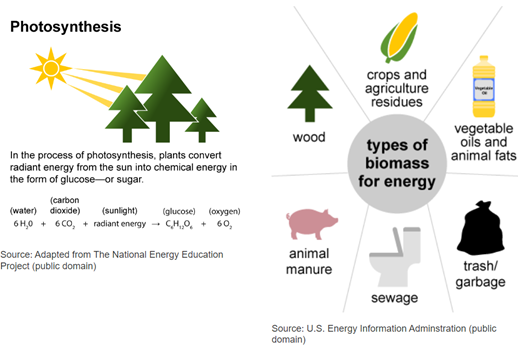
Figure 3: Photosynthesis is explained and examples of biomass are shown.
“Biomass was the largest source of energy in the United States up until its peak in 1870, when 70% of energy came from wood. … Coal and later petroleum, quickly replaced wood as the leading source of energy.” There is a debate about whether or not biomass energy is carbon neutral. Environmentalists are concerned that it is not clean energy.8
Biofuels are created from biological materials like plants, animals, wastes and microorganisms. We are most familiar with wood as a biofuel burned for heat and cooking. Biofuels can be solid, gaseous, or liquid. “Biofuels are everlasting and renewable resource because they are incessantly refilled.” (Datta, Hossain, and Roy 2019) There are many different types of biofuels. We can use corn to produce ethanol to power our cars. Unfortunately, this may have a negative effect on food prices. Using corn to make fuel instead of feeding people can drive up the price. Another way that biomass is used as an energy source is converting vegetable oil into biodiesel. If starting with used vegetable oil, first strain it to remove any left-over food pieces. Next, the process of transesterification converts fats and oils into biodiesel and glycerin. Using base ten ratios, if you were to take 100 pounds of oil and add 10 pounds of a short-chain alcohol (methanol) with a catalyst like sodium hydroxide (or potassium hydroxide). Dissolve the sodium hydroxide into the methanol and agitate. Then add them to the vegetable oil and continue to agitate. Allow the mixture to sit overnight so that they separate into biodiesel and glycerin. The glycerin will settle to the bottom and the biodiesel can be poured off the top. Using our base 10 ratios, this will result in 100 pounds of biodiesel and 10 pounds of glycerin.7
Nuclear
Nuclear energy is clean energy but has an unfavorable waste product. It can be costly to build a nuclear power plant and currently they operate for only about 30 years. Additionally, uranium is not an unlimited resource, and the increase usage of nuclear energy may deplete the resource. “Nuclear power plants have generated about 20% of the United States’ electricity since 1990”8 The United States uses nuclear power more than any other country. There are 28 states that use nuclear power, operating 54 nuclear power plants.
The basic parts of a nuclear power plant consist of a reactor where the nuclear fission takes place. There can be as few as one reactor and up to six reactors. The electricity is generated in the machine room from steam that powers a generator. The electricity that has been generated is transported and/or removed through the outlet power lines. Lastly, the cooling tower is located near a large body of water and is used for cooling the steam back to water.9
Nuclear power uses heat made from atomic fission to boil water and produce pressurized steam. The steam is routed to spin turbine blades attached to a generator to produce electricity. Nuclear fission splits atoms when a neutron smashes into a larger atom causing excitement and the atoms split into smaller atoms. Extra neutrons are also released causing a chain reaction. When atoms split, a very large amount of energy is released.10
Nuclear reactors use small uranium pellets placed in metal tubes. The tubes are immersed in water forming a circuit. The water heats to about 320 oC and kept under pressure to remain a liquid. This hot water is used in a steam generator to drive steam turbines and turn a generator creating an electric current. The resulting electricity can be as much as 400,000 volts and transported to the power grid. The steam from the generator has to be cooled and transformed back into water. A condenser uses cold water from the sea, a river, or cooled in an air-tower. This is why many nuclear power plants are located near a large water source. Nuclear power has no harmful emissions into the atmosphere.11
There are different types of nuclear reactors. The pressurized water reactor is the one I just explained. Eighty percent of the world’s nuclear power plants use this type of nuclear reactor. They have an excellent safety record. Twenty-two percent of the world’s nuclear reactors are boiling water reactors. These reactors do not have a secondary cooling circuit. The steam is led directly to the turbines. This type of reactor is more efficient and use less water. Heavy water reactors use a pressurized heat transfer fluid and a heavy hydrogen isotope known as deuterium. Fast neutron reactors use a closed fuel cycle that burns plutonium and reduces the amount of long-living radioactive waste. Gas-cooled reactors use helium to transport heat and are used in smaller power plants. There are new technologies being researched for smaller adaptations of nuclear power. These smaller reactors have improved safety and more resistant to nuclear accidents. They can also use fuel more efficiently and reduce the amount of radioactive waste.11
Unfortunately, there have been nuclear disasters like Three Mile Island in Pennsylvania in 1979, Chernobyl in Ukraine in 1986, and Fukushima in Japan in 2011. All of these resulted in radioactive material being released in the environment. Events such as these make people wary of nuclear power as an energy source. Additionally, the radioactive waste and used reactor fuel can remain radioactive and dangerous to humans for thousands of years. There must be a commitment to the proper handling, transportation, storage and disposal of these waste products to protect human health and the environment. Currently, there is no long-term solution that can guarantee long-time safety.

Comments: