Equivalent Fractions
Equivalent fractions are fractions that represent the same number. Equivalent fractions represent the same point on a number line. When students model 1/2 = 2/4 on the number line, both fractions represent the same length unit. You can find an equivalent fraction for any given fraction by multiplying or dividing both the numerator and the denominator by the same number. “This is the Identity Property of Multiplication, which states that Nx1 = N. For instance, since 2/2 = 1 and 1/2 X 2/2=2/4, then 1/2 and 2/4 are both equivalent fractions.”3
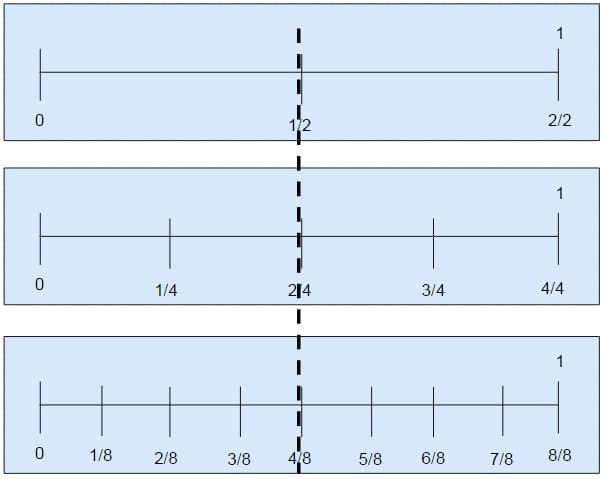
We will investigate several different strategies for helping students to grasp the principle stated formally above. Below is a diagram that shows equivalent fractions for 1/2. Number lines can be used to show equivalence by adding partitioning lines. In order to find an equivalent fraction for 1/2, the distance between 0 and 1/2 could be divided in half the distance and the distance between 1/2 and 1 could also be divided in half. Now the distance between 0 and 1 is divided into four equal lengths, so each of these is 1/4. Students will be able to see that 1/2 can be also called 2/4 because two of the lengths of 2/4 make the whole, so 2/4 satisfies the definition of 1/2.
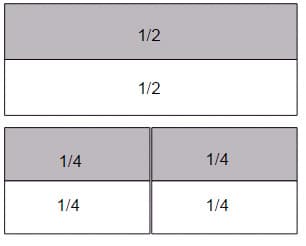
Equivalent fractions can also be found using the area model. When a rectangle is divided into two equal parts and one part is shaded, one of those parts is 1/2. When the rectangle is divided in half again, creating four equal parts, students can see that each of the 1/2s is made of 2 1/4s. This means that 2/3 equals 1/2. These fractions are the same because they represent parts of the rectangle of equal sizes.

Comments: